Skip to content
 [8]
[8]
 [9][10]
[9][10]
 [11][12][13]
[11][12][13]
 Download Now
Download Now
 Source: [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17]Source: [11]
Source: [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17]Source: [11]
 Source: [21]
Source: [21]
MyJobee Newsletter!
Industry insights & trends for Blue & Grey Collar workforce.
Subscribe to get our Newsletter
Edition 4, 2025
Edition 3, 2024
Edition 2, 2024
Edition 1, 2024
Edition 4, 2025
Edition-4, 2025
Industry insights & trends for Blue Collar workforce
The Transformative Impact of AI Evolution
- AI’s evolution is set to contribute a substantial $19.9 trillion to global economy through 2030 while driving 3.5% of global GDP. [1, 2]
- As a result, 98% of business leaders regard AI as a priority for their organizations, leading to job impacts across all regions of the globe. [1]
- AI is projected to impact nearly 40% of jobs worldwide, with some positions being replaced and others being complemented. [2]
- Generative AI can eliminate mainly white-collar roles, but it may also affect blue-collar fields like retail, manufacturing, agriculture, and food processing. [3]
- According to Pearson, generative AI could handle about 30% of white-collar roles, but less than 1% of blue- collar jobs. [4]
- On the positive side, 35% of top growing jobs are blue-collar roles, with over 1.7 million positions projected by 2032. [5]
- The global AI skills gap could lead to a significant labour shortage in the coming years [6], while India’s AI talent pool struggles to keep pace with the rapid growth of its AI market. [7]
Some Key Statistics on Blue-Collar Domain in AI
 [8]
[8]
 [9][10]
[9][10]
 [11][12][13]
[11][12][13]
Positive Impact of AI on Blue-Collar Domain
New Job Role Creation
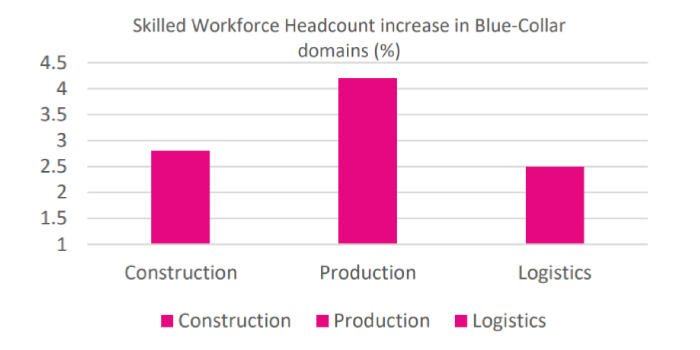
- AI-driven. AI can lead to the creation of 1.7 million new bluecollar jobs over the next 10 years [14] in different sectors by 2025 [15] including Construction [16], Manufacturing [17], Retail [18], Transportation [19] and Agriculture [20].
Enhancing Workspace Safety
- AI contributes to safer workplaces by providing real-time insights, risk assessment, and behaviour monitoring [21][22].
- AI can help transform frontline workers – drivers, mechanics, construction workers, service technicians – by making them better and safer. [23]
Increase Productivity and Efficiency
- Frees workers to focus on complex activities, boosting productivity in industries like manufacturing, logistics, and construction. [24]
- Improved efficiency in the workplace by reducing human errors and speeding up processes [25].
Re-Skilling Opportunities
- Globally, up to 375 million workers need to be AI-skilled by 2030 [26].
- Re-skilling opportunities offer workers a pathway to better job security and career advancement [27].
Other Impacts
- AI plays a pivotal role in redefining work-life balance [28].
- Reducing stress by automating repetitive tasks [29].
- Realistic training experience with AI-powered simulations [30].
Negative Impact of AI on Blue-Collar Domain
Job Displacement
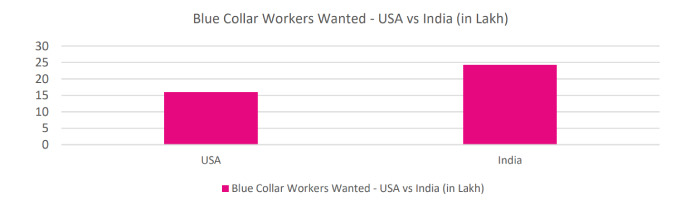
- AI-driven automation (e.g., robotics) is replacing repetitive blue-collar tasks in manufacturing and logistics, threatening millions of jobs in India’s 300-450 million-strong workforce [31].
Skills Gap
- Many blue-collar workers lack training to adapt to AI technologies, with only 5% of India’s workforce formally skilled, risking unemployment as automation grows. [32].
Economic Inequality
- AI eliminates middle-skill jobs (e.g., machine operators), polarizing the job market and widening income gaps between low-skilled workers and high-skilled professionals. [33].
Worker Uncertainty
- Fear of job loss due to AI, coupled with high turnover rates (15% monthly in some sectors), destabilizes India’s blue-collar workforce. [34].
Observations
- The Blue-collar job market is undergoing a remarkable resurgence, often referred to as the “Blue Collar Recruitment Boom” [35][36].
- AI & Robotics threaten Blue-collar jobs [37]. However, right now the percentage of risk of blue-collar jobs being automated is very less [38].
- The Government should take radical actions to save jobless Blue-collar workers from severe economic damage [39].
- AI is making Blue-collar workers’ job safer and more accessible [40].
- Companies need to create a culture of continuous learning and AI-upskilling to take advantage of potential gains in productivity [41].
Edition 3, 2024
Edition 3, 2024
Industry insights & trends for Blue Collar workforce
Revenge of the Blue-Collar Workforce
The phrase “Revenge of blue-collar workers” in the Indian context reflects a significant shift in the perception and status of blue-collar labourers.
- Economic Resilience: Demand for blue-collar workers has remained strong even as layoffs in white-collar sectors have increased [1, 2].
- Cultural shift: Blue-collar work is beginning to be seen as honourable and essential in India [3].
- Re-evaluation of ROI on College Degree: The narrative that a university degree guarantees a successful career is being challenged. As blue-collar jobs gain prominence, particularly those industry specific skills, the traditional view of employment is shifting [4].
- Social justice & empowerment: Movements advocating for better rights and recognition are gaining momentum, reflecting a desire for social justice and improved living standards for the bluecollar workers [5].
- Online Job Platforms: Similar to the white-collar workforce, online platforms are now connecting employers with blue-collar workers in a trusted and transparent way [6, 7].
Government and Private Initiatives for Blue-Collar workers :
- In the Union Budget 2024-25, the government has introduced a new skilling initiative aimed at training 20 lakh youth by 2029 [8].
- Government of India’s eShram project is expected to be bring unorganized blue-collar workers under social security [9].
- Private companies are investing in employee (including blue-collar) benefits despite constrained budgets – report by Plum [10].
- Companies are taking various initiatives to upskill their bluecollar workforce [11].
- Recruiting firms are digitizing records & databases for blue-collar workers to implement a seamless & efficient recruitment process [12].
- Only 1% of blue-collar jobs are currently at the risk of being automated by AI. For white-collar workers, the percentage is much higher. [13].
Female participation – Initiatives, Challenges & Potential
- The government’s initiatives, such as establishing working women’s hostels and crèches, not only ensure safety but also provide financial incentives, thereby promoting higher participation of women in the workforce [14].
- 73% of the Indian companies are focusing on encouraging women’s progression into senior leadership roles [15].
- Increasing women’s participation in the labour force could unlock over 70% of the potential GDP growth [16].

Other Issues Still Pending Resolution
- Average Salary: Average salary of Indian blue-collar workers is much less in comparison to the blue-collar workers in USA & China [17, 18, 19]. More than 58% of blue-collar workers earn less than Rs. 20,000 per month [20].
- Social Security Benefits: Only a small portion of full-time blue-collar workers can access the benefits of EPF and ESIC programs, that are not accessible to the informal sector workers [21].
- Employee Attrition: Companies are increasingly focusing on employee engagement policies to reduce the average monthly attrition rate of 8-24% for blue-collar workers [22].
- Shortage of Skilled Workers: Irrespective of several upskilling initiatives taken for blue-collar workers, the current workforce faces a substantial skill gap [23].
- Skill Gap: The skill gap between the skills demanded by industries and the skills possessed by the bluecollar workforce limits upward mobility and earning potential [24].
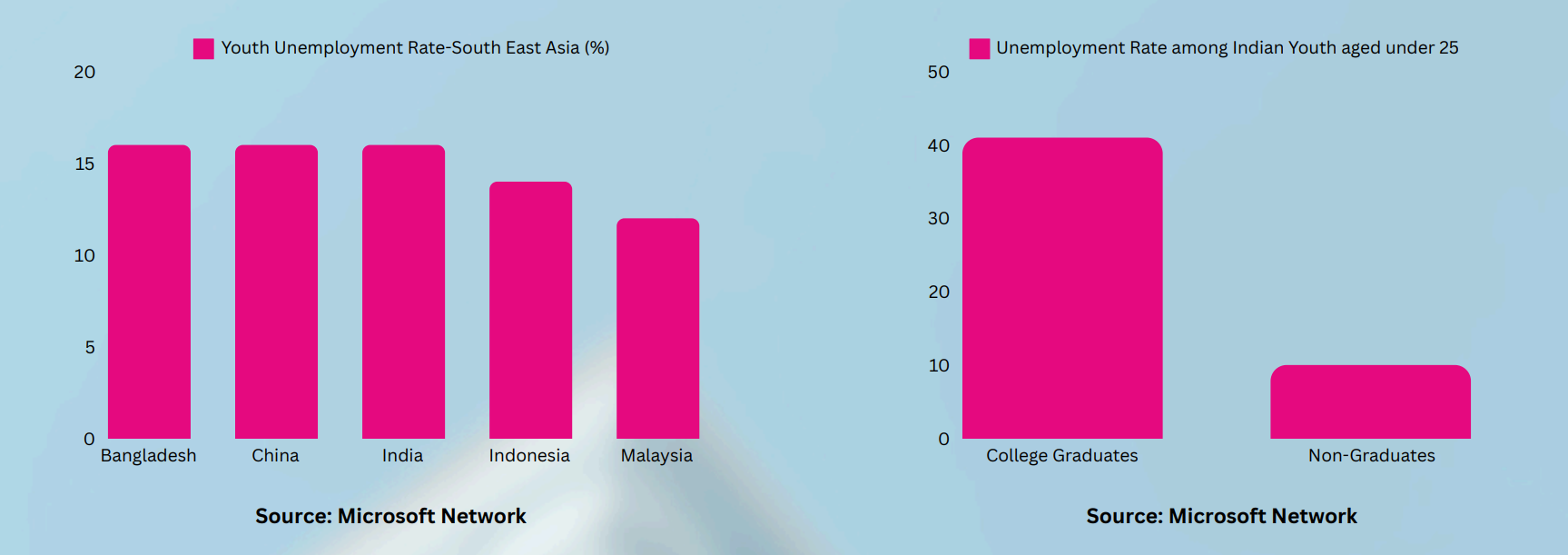
Youth Unemployment: A Threatening Crisis for Asia’s Economic Stability
 Download Now
Download NowEdition 2, 2024
Edition 2, 2024
Industry insights & trends for Blue Collar workforce
The Risk Ahead
- India is projected to become the world’s 3rd largest economy by 2027 [1].
- The economy of any country is vastly dependent on the contribution of the Blue-collar workers [2].
- India is witnessing a 7% growth in Blue-collar job vacancies [3].
- Around 300 Million of the total workforce India are blue-collar workers [4].
- Roughly 80% of jobs in India are Blue-collar jobs [5].
- Key economic sectors are experiencing 30% demand-supply gap for the Blue-collar workers [6].
- India to a fill a shortage of 150 Million skilled workers [7].
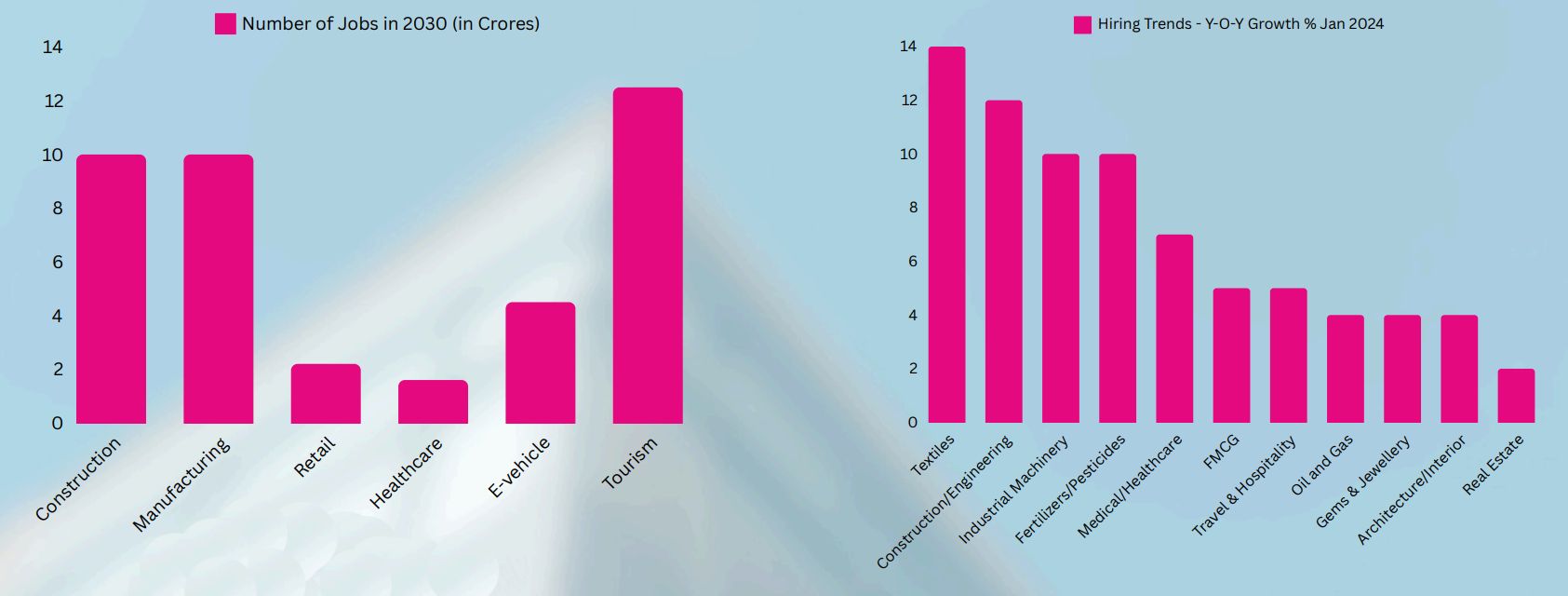
At a Glance: Demand vs Shortage
Demand (2023-24)
- 7.50% Growth in hiring [3]
- 5-6 Million Electronics manufacturing Blue-collar jobs in 2026 [5]
- 71 Million Construction sector vacancy [8]
- 35 Lakh Jobs in Infrastructure [9]
- Manufacturing Industry jobs [10]
 Source: [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17]Source: [11]
Source: [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17]Source: [11]
Shortage (2023-24)
- 150 Million Skilled worker shortage [7]
- 76% Manufacturers reported skilled labour shortages hurting profitability [19]
- 10 – 30% Labour demand supply gap [7]
- 80% Employers struggling with talent shortage [20]
- 22 Million (5G Telecom) Skilled workers needed including Blue-collar by 2025 [18]
- 28% Organizations Witness production delays at least once in every 2 weeks due to shortage of labour [19]
 Source: [21]
Source: [21]
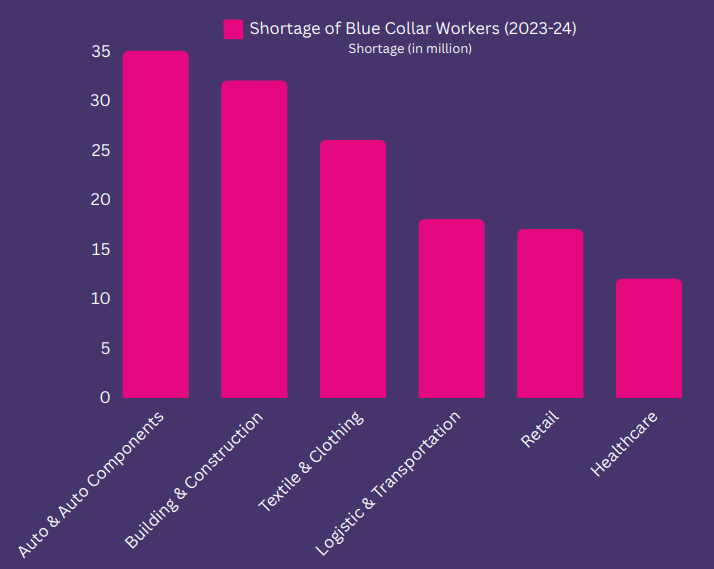
Bridging the Skill Gap: Building a Skilled Blue-collar Workforce
- Government of India activities like Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) and the Expertise India Mission for upskilling Blue-collar workers [22].
- MyJobee India has made their Commitment by giving instructive back & ability improvement preparation to the underprivileged children of blue-collar workers.
- Tata Engines has executed preparing program in EVs (Electronic Vehicle) and other cutting-edge innovations for their employees [23].
- Northern Locale Cultivate Apparatus Preparing and Testing Established (NRFMTTI) has built a association with Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd to fortify the Blue-collar workforce in cultivate mechanization [24].
- Honda India Control Items (HIPP) has Ability Olympiad to upgrade the specialized expertise of their employees [25].
- Times OOH is taking after the approach of teaching and raising mindfulness among Blue-collar workers [25].
- Chaabi, an HRTECH company, employs AI-powered vernacular learning strategy to upskill blue-collar workers [26].
- Mahindra & Mahindra prepares blue-collar laborers in mechanical autonomy, computerization, & mechatronics through its skill development centre [27].
- Vedanta Ability School for Brilliance offers professional preparation in exchanges important to the mining industry [28].
Priorities
- Initiating upskilling program
- Offering career development opportunities
- Improving workplace safety
- Enhancing employee engagement & wellbeing
- Prioritizing physical & mental wellbeing
Edition 1, 2024
Edition 1, 2024
Industry insights & trends for Blue Collar workforce.
Market Trends
- Hiring intent for non-white collar jobs was up 10% YoY in Q1FY24.
- According to a report by McKinsey & Company, India is expected to create 90 million new jobs by 2030. Of these, 70% are expected to be blue-collar jobs.
- There has been an increase in the migration of blue-collar workers from India to the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) nations in 2023.
- Soon, Korea will sign a pact with India to source skilled manpower and open doors for blue-collar workers.
- Germany is looking to source workers from India to address skills shortages.
At a Glance :
- A survey reported by NEWS18 has revealed that blue-collar jobs will grow by 12% in2023 as compared to 2022.
- Annual Blue-Collar Job market index highlights 50% Growth in Hiring trends from 2022 to 2023
- Blue-collar job vacancies grew 7% in March to 57,11,154.
- Blue collar workers in India increased from 232 million in 2017-18 to 243 million in 2021-22 indicating growth rate of 4.7% per year.
- Apple became the largest blue-collar Job Creator in India’s electronics Industry with 1 lakh new Jobs.
Insights and Observations
- Increasing demand for blue-collar workers in India.
- Enough skilled blue-collar workers are not available in the market.
- Technology may not directly increase wages, but it can help workers be more competitive and access new work opportunities.
- This is particularly important for women, who are looking for new opportunities to contribute to their family income, with
signs of a looming recession. - Most blue-collar jobs are going to freshers with tech skills.
- As the Indian economy becomes more complex and sophisticated, there is a growing demand for skilled blue-collar workers.
- This is particularly true in sectors such as manufacturing, construction, and IT. Therefore, available blue-collar workers need
to be upskilled to become job-ready. - Wages for blue-collar workers should be at par in comparison to other countries to prevent migration of blue-collar workers.
- Participation of women as blue-collar worker should be increased across various sectors.
Increasing demand of blue-collar workers in India
The blue-collar workforce in India is an important part of the economy, comprising more than 80% of the
total workforce. These workers are essential for the functioning of several sectors, including manufacturing,
construction, transport and logistics. However, the current situation of blue-collar jobs in India is
characterized by a complex combination of factors, including
- Increasing demand: The Indian economy, according to IMF estimates, will emerge as the world’s third largest economy by 2027°This growth is fueling the demand for skilled blue-collar workers in different sectors.
- E-commerce boom: As per a report by Statista, the Indian E-commerce Market is expected to reach $200 billion by 2027 from $22 billion in 2018. This growth is creating new opportunities for blue-collar workers in the logistics sector.
- Skills shortages: India presents a paradox of skill shortages despite a situation of labor surplus, which threatens the growth story. There is a need for 33 million skilled workers in building and construction and 18 million in transportation and logistics.
- Technological advances: According to a World Economic Forum report, automation would certainly provide
millions of new job possibilities in the future. However, even in blue-collar jobs, professionals will be required
to have a working grasp of novel technology such as Al, ML, and data analytics.
Current status of skilled-labour in blue-collar domain
- Due to an acute shortage of skilled labour in the frontline or blue-collar workforce, the companies across different sectors are hiring more apprentices to make them job ready.
- According to a recent report by the World Economic Forum, India needs to skill or upskill over 400 million
workers by 2030 to meet the demands of the changing economy. The report also highlights that the
demand for skilled blue-collar workers is expected to grow by 25% in India over the next decade. - According to Harsh Goenka, RPG Group Chairman, the key issues that are affecting his business are:
shortage of skilled construction workers, truck drivers, and plantation workers. - There has been a 50% increase in the migration of blue-collar workers from India to the Gulf Cooperation
Council (GCC) nations in the first seven months of 2023, according to a study conducted by Huntr, a United
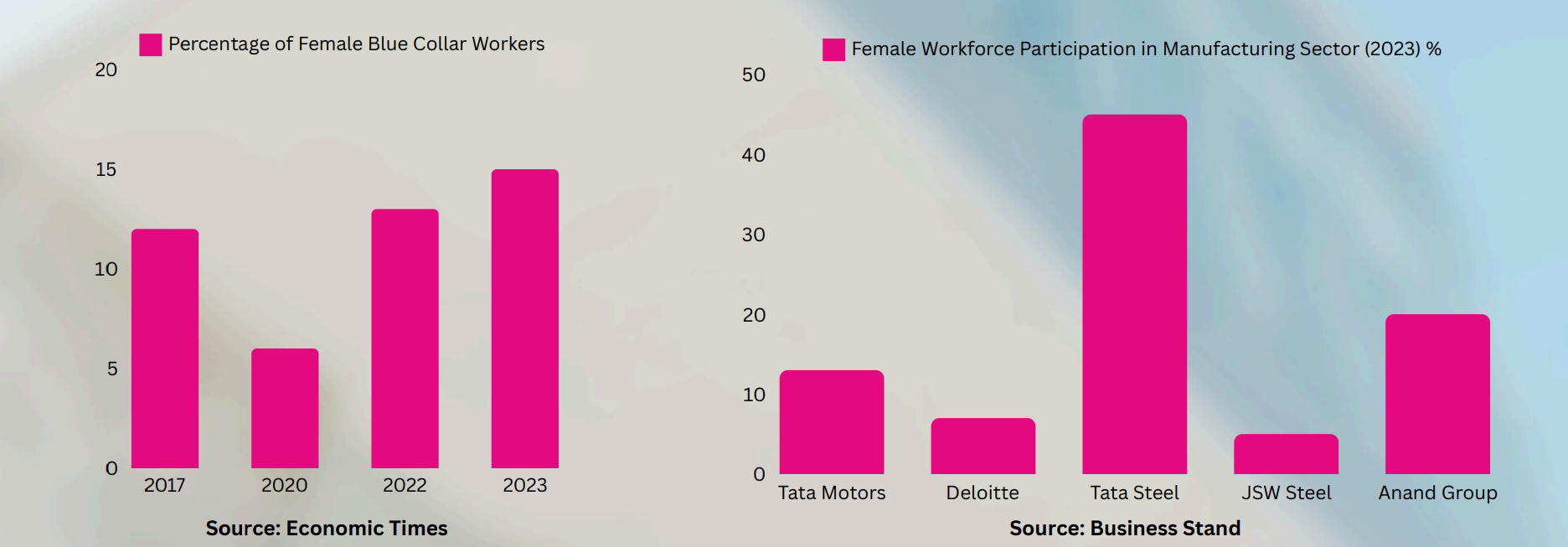
Arab Emirates-based marketplace connecting migrant workers with enterprises. - Deloitte’s Blue Collar Workforce Trends Report 2023 shows that the current female blue collar work force participation is at 8 per cent (1in 12), a rise from <2 per cent a couple of decades earlier.
Government of India initiatives to counter the skill shortage
- Atmanirbhar Bharat Rojgar Yojana (ABRY) to incentivize employers for creation of new employment along with social
security benefits and restoration of loss of employment during Covid-19 pandemic. - Pradhan Mantri Rojgar Protsahan Yojana (PMRPY) to incentivise employers for creation of new employment.
- National Career Service (NCS) Project for transformation of the National Employment Service to provide a variety of
career related services like job matching, career counselling, vocational guidance, information on skill development
courses, apprenticeship, internships etc. - Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) is a Skill Certification scheme with the objective of enabling Indian youth to take up industry relevant skill training that will help them in securing a better livelihood.
- Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme across 14 key sectors, to create national manufacturing champions and to create 60 lakhs new jobs.
- The National Industrial Corridor Development Programme is India’s most ambitious infrastructure programme aiming to develop futuristic industrial cities along with creating employment opportunities and socio-economic development.
- The Centre’s Budget announcement to boost capital expenditure during 2023-24 by 33 per cent to Rs 10 lakh crore is likely to drive up blue-collar job creation.
- The Indian government is taking steps to formalize the blue-collar workforce Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Maan-dhan (PMSYM) scheme and the Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO).
Sources and References
- India economic outlook, Dr. Rumki Majumder, Deloitte Global Economics Research Center, October 2023
- How E-commerce boom is shaping the logistics industry in India? LinkedIn, Nov 30, 2022
- Skill shortages: Unless it is addressed through scaling up training programmes, it will hit India’s growth, Financial Express, Oct 11, 2023 [4] How Technology Can Revolutionize Blue-collar Workforce Management? Startup Talky, Jan 28, 2022
- Short of skilled hands, companies turn to apprentices, By Rica Bhattacharyya, The Economic Times, Nov 29, 2023
- “Demystifying India’s Blue-Collar Skilling Landscape: Data and Insights”, Linkedin
- India’s unemployment crisis: Harsh Goenka highlights how shortage of skilled workers threatening Indian job market, Livemint, Aug, 2023
- 50% jump in blue-collar worker migration from India to Gulf nations; UP tops list, MONEYCONTROL NEWS NOVEMBER 17, 2023
- Number of women in blue-collar jobs increasing across manufacturing sector, Business Standard, Dec 3, 2023
- https://labour.gov.in/aatmanirbhar-bharat-rojgar-yojana-abry
- https://labour.gov.in/pradhan-mantri-rojgar-protsahan-yojanapmrpy
- https://www.ncs.gov.in/
- https://www.pmkvyofficial.org/home-page
- https://www.investindia.gov.in/production-linked-incentives-schemes-india
- https://www.nicdc.in/
- Business Today February 7, 2023
- Business Standard, Apr, 2023
- Soon, Korea to sign pact with India to source skilled manpower, open doors for blue-collar workers, Asian Community /news (ACN) Network, 9 Jul, 2023 [19] Germany looking at sourcing workers from India to address skill shortages, TIMESOFINDIA.COM/Updated: Mar 13, 2023
- Education and Careers Desk, News18.com, Last Updated: JANUARY 18, 2023,
- 14 September, 2023by BW Online Bureau
- The economic Times Apr 25, 2023
- Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy, https://www.cmie.com, 24 Inc42 Mar, 2023
- World economic forum Apr, 2023
- business insider India, Apr 2023
Contact Us